Treatments
Paediatric & Adult Fracture Management
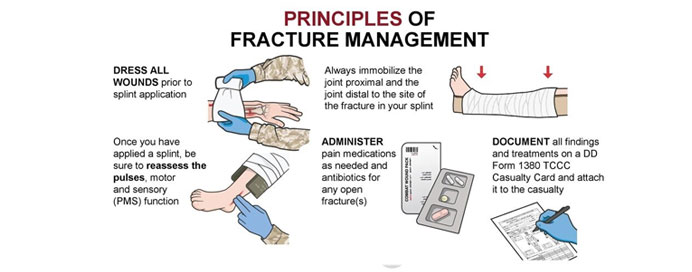
Fracture management differs significantly between paediatric and adult patients due to variations in bone structure, healing potential, and treatment approaches. In children, bones are more flexible, have a higher remodeling capacity, and often heal faster. Growth plate involvement is a key concern in paediatric fractures. In contrast, adult bones are more rigid, have a lower healing potential, and are more prone to complications like delayed union, non-union, and osteoporosis-related fractures. Treatment strategies for both groups include conservative methods like casting and splinting, as well as surgical interventions such as internal fixation or external fixation when necessary. The goal in both cases is to achieve proper alignment, stability, and functional recovery while minimizing complications.
Paediatric Fracture Management
- Bone Characteristics – More porous, flexible, rapid healing, and presence of growth plates.
- Common Fracture Types – Greenstick, buckle (torus), plastic deformation, and physeal (growth plate) fractures.
Adult Fracture Management
- Bone Characteristics – Less flexible, slower healing, prone to osteoporosis-related fractures in the elderly.
- Common Fracture Types – Complete fractures, stress fractures, intra-articular fractures, and osteoporotic fragility fractures.
- Higher reliance on surgical intervention (ORIF, external fixation, intramedullary nailing) due to reduced healing potential.
- Rehabilitation & physiotherapy play a crucial role in functional recovery.
Copyright © Dr. Tushar C Patil 2025 All Rights Reserved.
